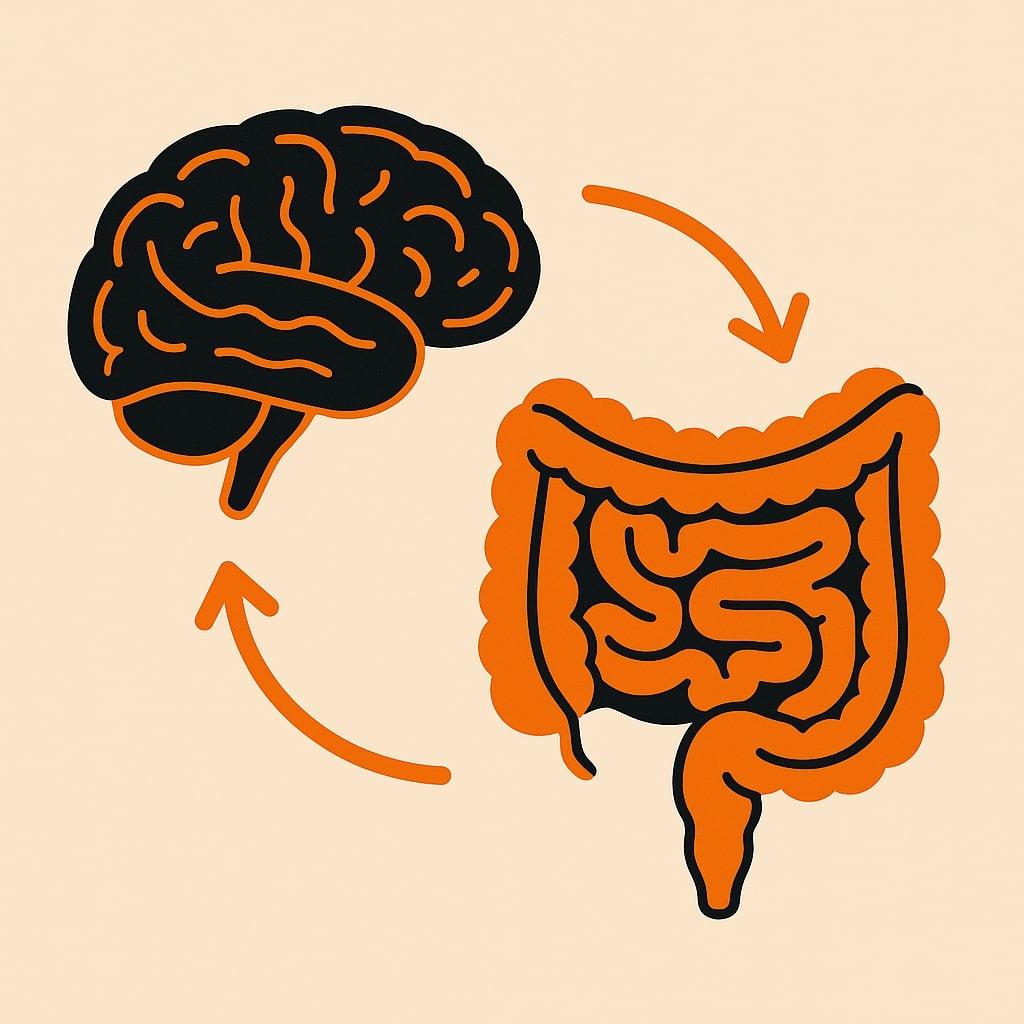
Gut-Brain Axis
What is the Gut-Brain Axis?
The gut-brain axis is the two-way communication system between your digestive system and your brain. They send messages through nerves, hormones, the immune system and the trillions of microbes that live in the gut. This link helps control mood, stress, digestion and even sleep [1][2].
What does the gut-brain axis actually do?
Think of your gut and brain as close teammates. They talk all day to keep your body in balance.
| How the messages travel between your brain and gut | Description |
| Nerves | The vagus nerve is like a phone line between gut and brain, carrying fast signals both ways. |
| Hormones and chemicals | The gut makes and reacts to messenger chemicals such as serotonin, which can influence mood and gut movement. |
| Immune system | Immune cells in the gut send alerts that can change how the brain and gut behave. |
| Gut microbes | Helpful bacteria and other microbes produce substances that can affect stress, appetite and inflammation. |
Learn how factors such as genetics, diet, lifestyle, age, mode of birth, antibiotic use and more can shape your microbiome and simple tips for how you can optimise it.
Why the gut-brain axis matters
Your gut can have a significant influence on your overall health including aspects such as:
- Digestion: Stress and emotions can change gut motility and sensitivity, which may affect bloating or bowel habits.
- Mood and focus: Gut signals can influence how calm, alert or irritable you feel.
- Sleep and energy: Gut hormones and microbes can nudge your sleep-wake rhythm and energy levels.
- Immunity: A healthy gut helps train the immune system to respond appropriately.
What are the symptoms of gut-brain issues?
Important: Ongoing pain, weight loss, blood in stool, persistent vomiting, fever or symptoms that wake you at night need medical advice. Speak to your GP or an appropriate healthcare professional.
Everyday ways to support a healthy gut-brain axis
Food and drink
- Eat plants often: Aim for a variety of fruit, veg, whole grains, nuts, seeds and pulses to feed helpful gut microbes.
- Include fermented foods: Options like live yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut or kimchi can add beneficial microbes.
- Steady meals and fibre: Regular meals and gradual increases in fibre support comfortable digestion.
- Hydration: Water helps fibre do its job and keeps things moving.
Mind and body habits
- Stress skills: Try breathing exercises, short walks, yoga or mindfulness for 5 to 10 minutes daily.
- Sleep routine: Keep a regular bedtime and limit screens before sleep.
- Gentle movement: Daily activity can calm the stress response and aid gut motility.
FAQs
Is it all in my head?
No. The gut has its own nerve network and chemical signals that influence real physical symptoms. The brain and gut affect each other in both directions.
Do I need a probiotic supplement?
Not always. Many people do well with a varied, plant-rich diet and fermented foods. Some probiotics may help in specific cases. If you are considering a supplement, ask a healthcare professional for personalised guidance.
Can stress really upset my stomach?
Yes. Stress can change gut movement and sensitivity, which may lead to cramps, urgency or bloating in some people.
Medical Disclaimer
This overview is educational and not a diagnosis. If you have ongoing symptoms, new symptoms or worrying signs, seek medical advice. A registered dietitian can help you build a simple plan that suits your lifestyle and medical needs.
Related terms
- Microbiome
- Vagus nerve
- Serotonin
- Fermented foods
- Mindfulness
Nutritionist's Corner: Final Thoughts
“The gut and brain are partners. Small daily habits make a big difference: eat a variety of plants, include a little fermented food, drink enough water, move your body and practise short, regular stress-relief. If symptoms persist or worry you, get tailored advice from a registered professional.”
— Yusra Serdaroglu Aydin, MSc RD
Vivere helps you take control of your health with personalised microbiome insights from state-of-the-art gut health testing, nutritional guidance, science-backed supplements (including NAD injections by Vivere) and expert support. Sign up today and start living better, for longer.
Sources
Author

Yusra Serdaroglu Aydin, MSc RD
Head of Nutrition and Registered Dietitian
Yusra is a registered dietitian with a multidisciplinary background in nutrition, food engineering, and culinary arts. During her education, her curio...